
VPN Client
Get private internet access and protect your online security

Get private internet access and protect your online security
Get from the App Store for free
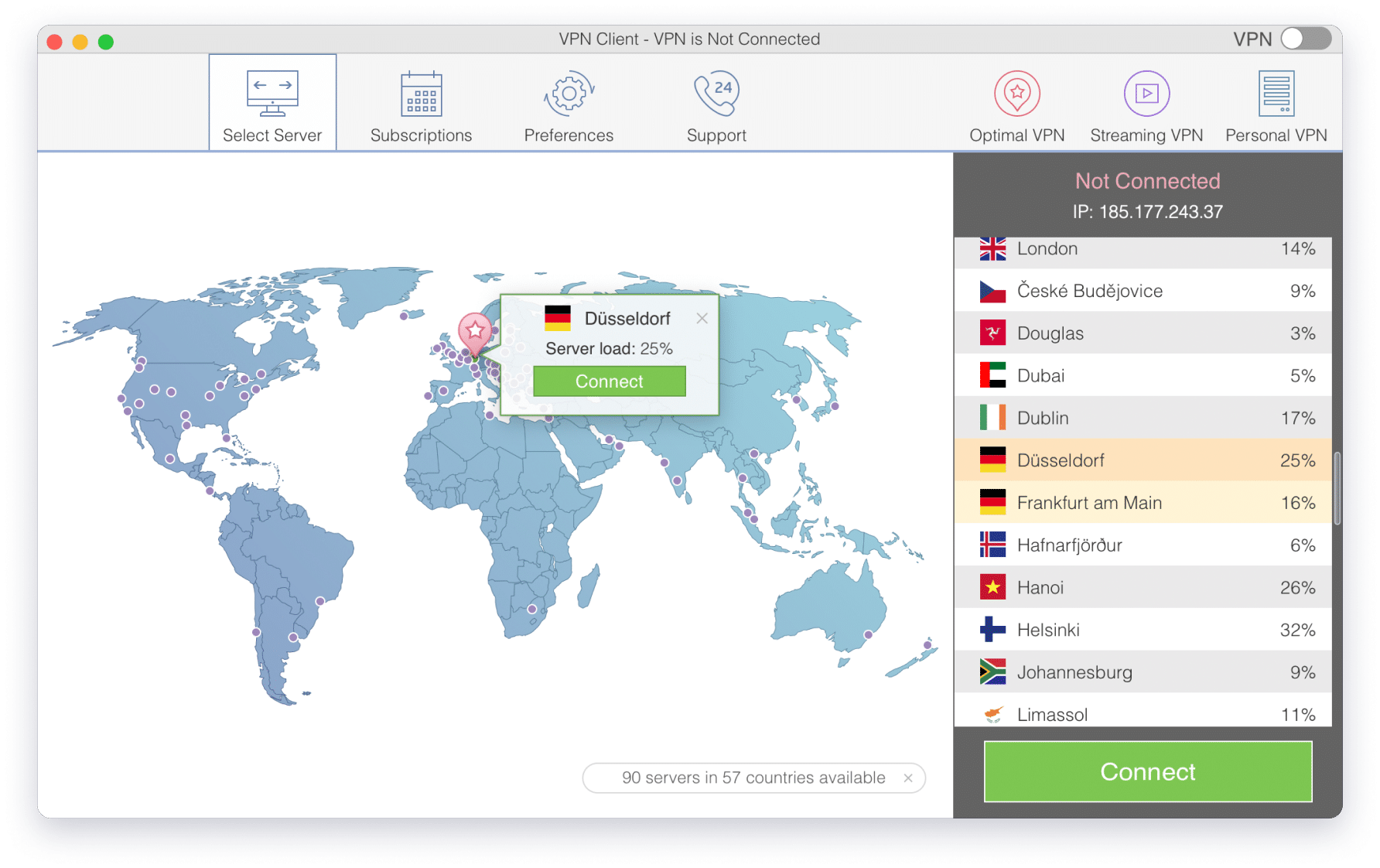
VPN Client – best way to keep your personal information safe from identity thieves and access restricted internet content globally
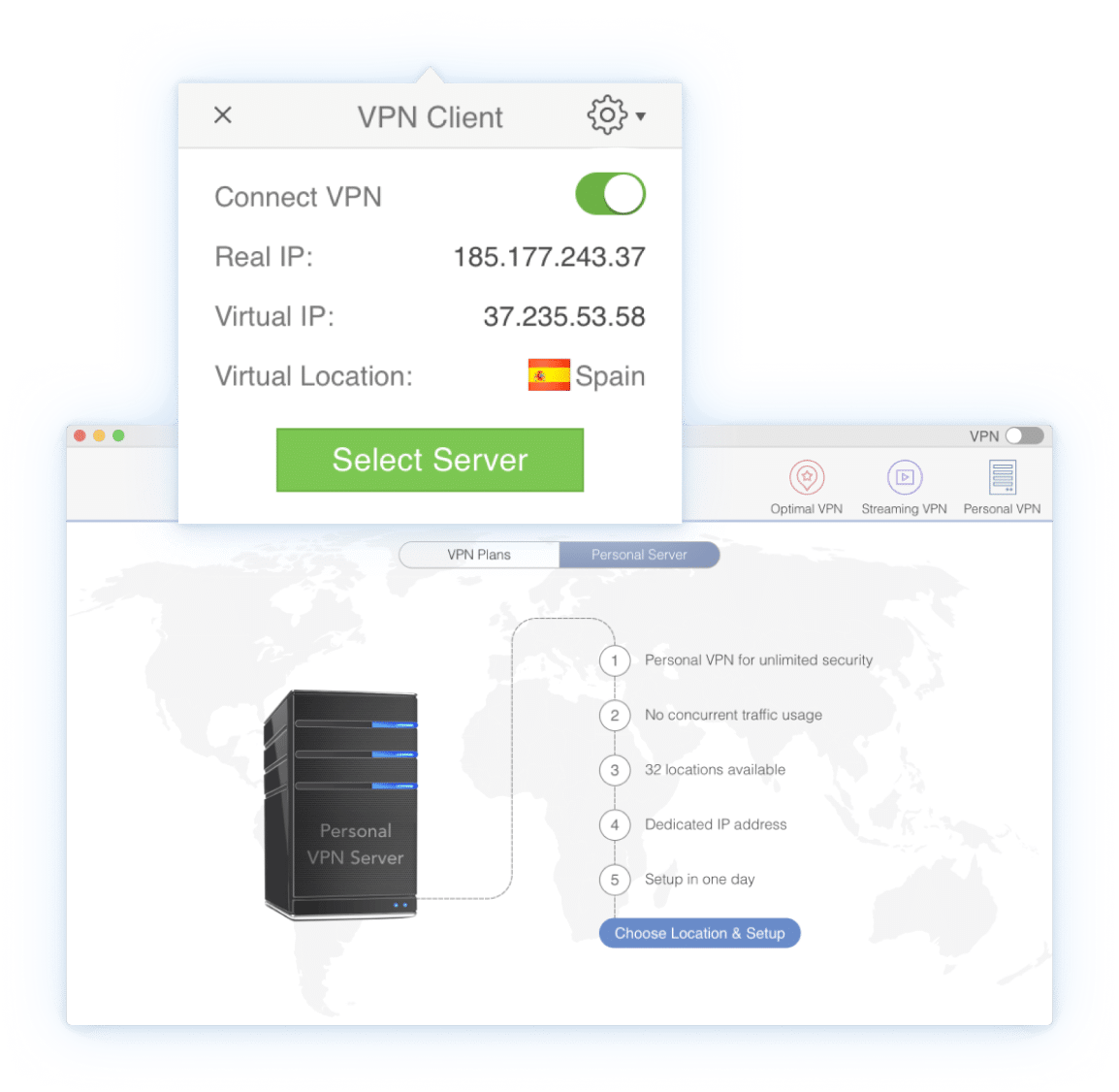
One click to connect to VPN
Fastest VPN speed
Completely secure servers
VPN Unlimited bandwidth
Strong encryption
No logging of your data
Free 7-days starter plan
Profitable pricing plans








3,99$
7 days
Save 47%
8,99$
1 month
Save 67%
16,99$
3 month
Save 81%
39,99$
1 year
Save 82%
109,99$
3 year