July 21, 2025
How to open Task Manager on Mac
If you have recently switched from Windows to Mac, you may find that most Windows keyboard shortcuts don’t work on a Mac. While navigating the Mac operating system does have its own method, most users find it intuitive and quick to learn.
The most frequently asked questions from new Mac users include:
- What is Control Alt Delete on a Mac?
- How to get Task Manager on a Mac?
- How to force quit on a Mac, and so on.
In this blog post, we will explain the Mac equivalent of the Windows Task Manager and how to view running processes in macOS.
What is the Control Alt Delete shortcode for Mac
Control-Alt-Delete is a shortcut to call the Force Quit command for programs on Windows.
For the macOS system, you should use the Command-Option-Escape shortcut to call the Force Quit Applications window.
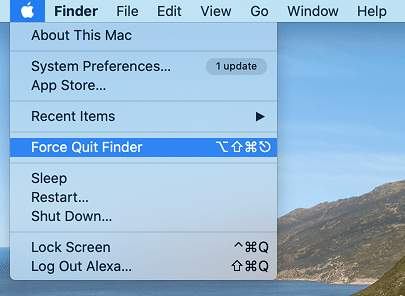
Also, you can get this window by clicking the Apple icon in the Menu bar and selecting Force Quit.
How to open Task Manager on a Mac
When an application freezes on Windows, the Ctrl-Shift-Esc command is used to bring up the Task Manager and quit the process in question. But how about on a Mac? How do you end processes that crash Safari or lock the machine up?
First, we would like to mention that the Mac equivalent of Task Manager is called Activity Monitor. Just remember that Apple Task Manager = Activity Monitor.
Use one of these two ways to open Activity Monitor on a Mac:
- Click Activity Monitor icon in the Launchpad.
- Use the Spotlight to quickly find Activity Monitor.
How to see which programs are running on your Mac
1. Use Activity Monitor
Even just one application or open process can significantly degrade your Mac’s performance. Activity Monitor helps to identify such programs among a dozen apps running in the background. The app lets you easily view active processes that are running on your Mac, manage them, and even quit tasks or applications.
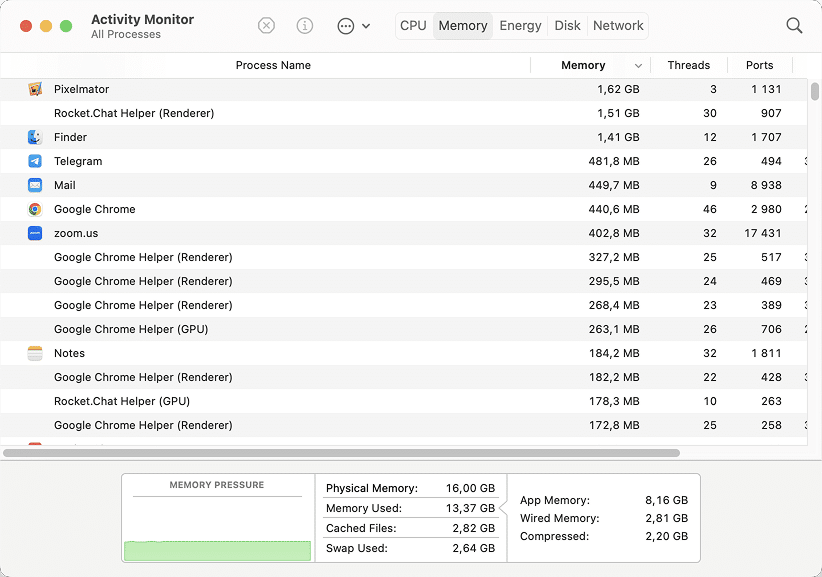
With Activity Monitor, you can monitor many parameters of the system, such as:
- CPU load
- RAM memory
- Energy used
- Disk space
- Network monitoring
2. Use Terminal to view a list of running processes
For those who prefer working with Terminal, there are simple commands to view the list of running programs. Just open the Terminal and type only one word:
TopCopy
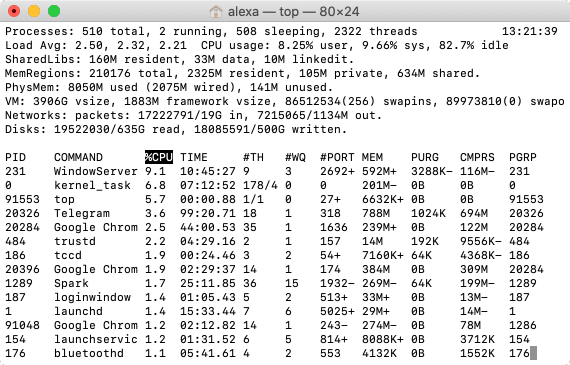
If you need to view a list of the most voracious applications that consume the most bytes, sort them by CPU:
top -o cpuCopy
Sort applications by memory usage:
top -p sizeCopy
How to use Activity Monitor on a Mac
Now let’s take a closer look at each parameter of open programs on a Mac. With help from Activity Monitor, we will identify the programs and processes that are consuming too much of your system’s resources.
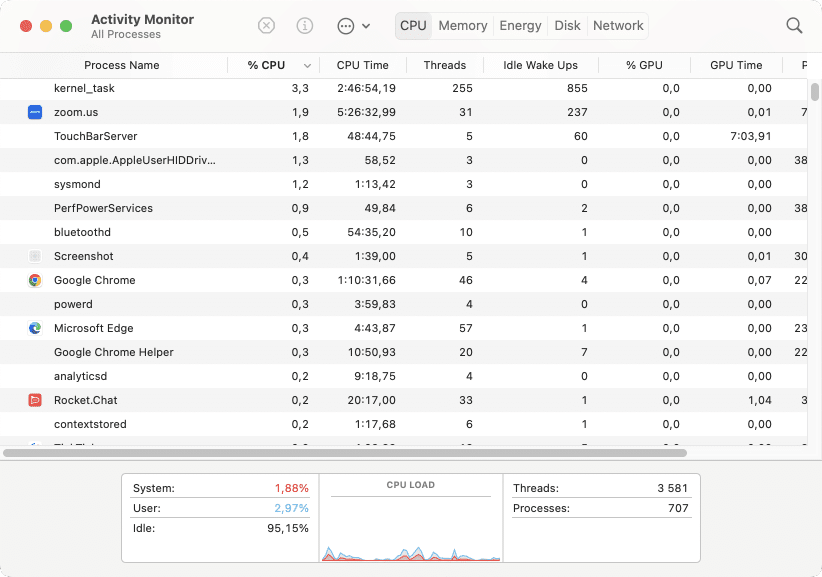
1. Check CPU usage on a Mac
If your Mac starts working too slowly, it overheats, the fans work continuously and make noise, and programs may freeze. Most likely there are some programs that are consuming a large portion of processor load. You can identify such programs with the help of Activity Monitor.
In this case, launch Activity Monitor and go to the CPU tab. Sort the list of programs by CPU column, find out the programs that use most CPU, and close such programs.
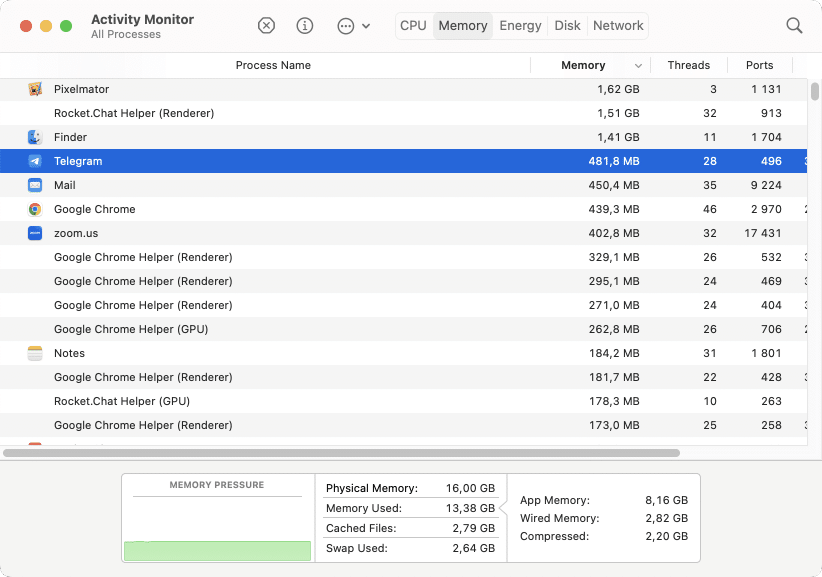
2. Check RAM usage on a Mac
If your computer is running slowly, there are several indicators that your Mac’s performance is due to limited RAM. One example is when programs work slowly and documents even open slowly, but without overheating or the fans making noise. In this case, there is most likely not enough free RAM on your Mac for your programs to function properly. To create more free space, find the programs that use the most memory and close unused ones.
In the Activity Monitor app, go to the Memory tab to see memory intensive Mac processes.
3. Find apps that are using and draining the most battery life
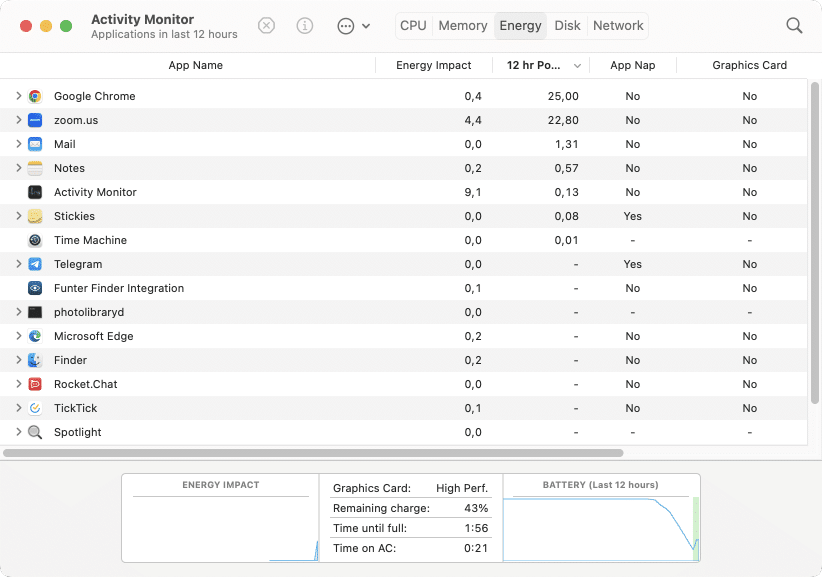
If your Macbook’s battery is draining very quickly, we recommend checking the programs which are using the most energy. To get this information, switch to the Energy tab within Activity Monitor.
Here you can find the data relating to how apps use your Macbook’s battery. Find the apps that are using the most energy, and if you don’t need them at the moment, close them.
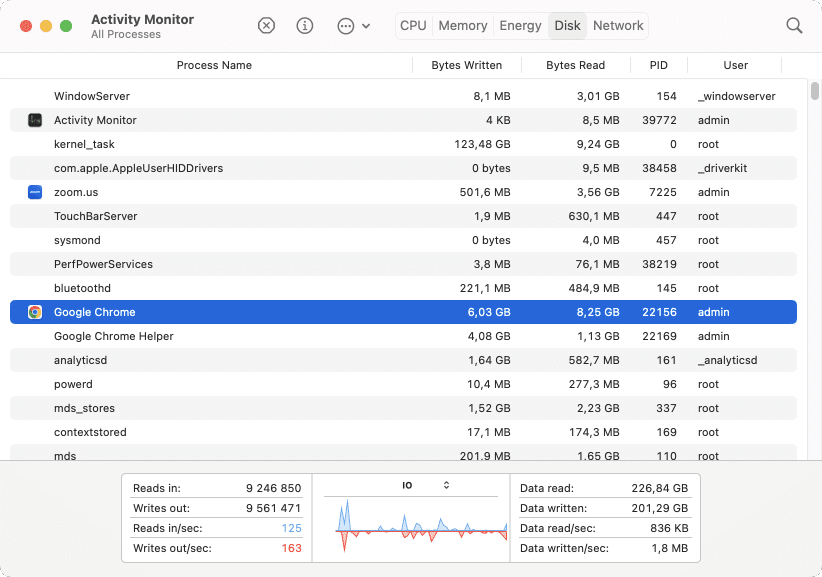
4. Check Disk activity on a Mac
Most users don’t need to worry about the Disk tab. This part of Activity Monitor allows users to troubleshoot or monitor real-time disk activity. Here you can check how much data is being written to and read from your Mac’s drive by different processes, as well as the number of times that your Mac accesses the disk.
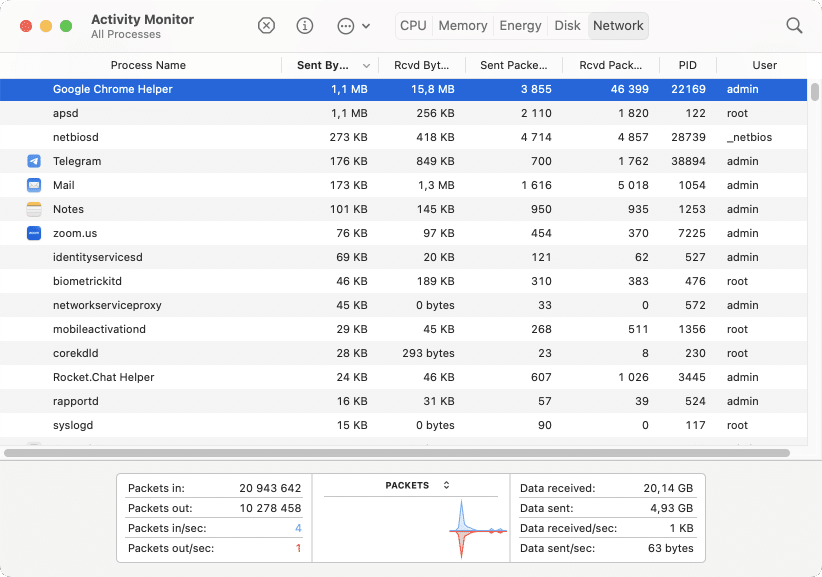
5. Check Network activity on a Mac
If you are having internet problems, if some network accounts are unavailable, or if network connections fail often, then you should check Network activity on your Mac.
Go to Activity Monitor’s Network tab to see how much bandwidth the processes are using. Then sort the programs by “sent Bytes” or “Read Bytes” to see the most active processes. Finally, close unneeded active programs.
Please note that not all programs can be closed, due to the fact that some of them are launched by the system and are required for its proper performance. If you see that these programs are using a lot of CPU, memory or energy, then we recommend just restarting your Mac.
How to force quit on a Mac
Whenever any application crashes on your Mac or it doesn’t respond for a while, you may need to force quit it. Here are several ways to do that:
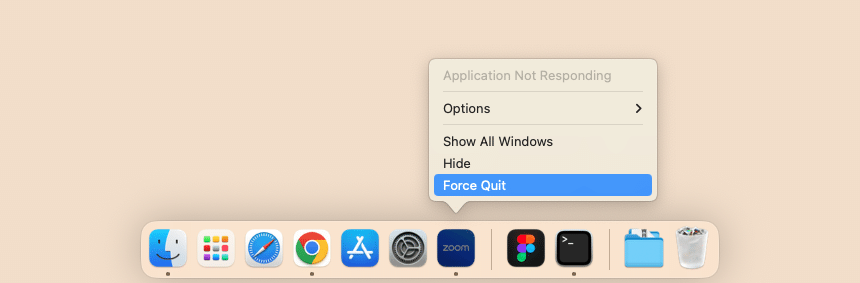
1. Use the Dock panel
Click the app’s icon in a Dock panel, hold the Option key and select Force Quit command.
2. Use the “Force Quit” dialogue
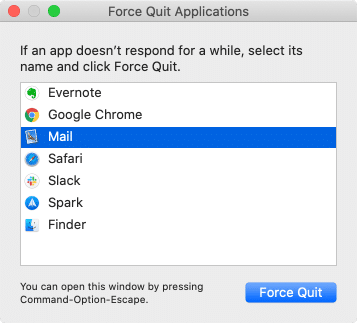
What to do when the Dock won’t pop up? A list of open programs can be also viewed via a “Force Quit” dialogue. There are two ways to open the “Force Quit” dialogue:
- Use the simple keyboard shortcut Command + Option + Escape.
- Or go to the System Menu → select Force Quit command.
Then select the app you want to stop and click on Force Quit.
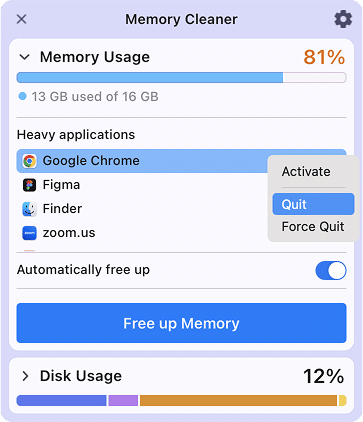
How to monitor memory usage with Memory Cleaner
In the previous paragraphs, we showed several ways to force close apps on a Mac in order to find out what apps are running. Now we would like to share an easy way to complete all these tasks and speed up your Mac in just one click. Simply use the free utility, Memory Cleaner.
Memory Cleaner can display the list of apps that use the most memory on your Mac, clear inactive RAM memory with just one click, and stop all running applications. With the app, you can get access to memory usage directly from the menu bar.
Conclusion
As you can see, there are various equivalents of macOS Task Manager, and Activity Monitor is one of them. It is a built-in utility that is used by most Mac users. However, if you want to monitor RAM memory usage and clear inactive RAM, we would recommend using the free Memory Cleaner app.