This article will explain how to format an external hard drive for a Mac to be able to use it on both macOS and Windows platforms. You will also learn what exFAT and NTFS formats are and which one you should choose depending on your needs.

Contents
- Why do you need to reformat an external hard drive for your Mac?
- What is the best format for an external Mac hard drive?
- How to format an external drive (USB) for a Mac
Before we start
Disk Space Analyzer will help you find what is taking up the most space on your disk, detect old and unused bulky content, and free up space on your disk.
Disk Space Analyzer
Why do you need to reformat an external hard drive for your Mac?
By default, most models of hard disk drives (HDDs) and solid-state drives (SSDs) are formatted for a Windows operating system. This often causes difficulties when opening external drives on a Mac. For example, if you buy a new HDD, you will most likely first have to format the external disk to be able to use it on your Mac.
Mac computers use a different file system called HFS+. There are also FAT32 and ExFAT formats, which are compatible with both operating systems. If you are only going to use the hard drive on your Mac, then you should choose the HFS+ format. If you want to be able to work with your hard drive on both Mac- and Windows-based computers, then you will have to choose other formats. Keep reading, and we will explain the differences between disk formats in more detail, as well as how to format a hard drive for your Mac.
What is the best format for an external Mac hard drive?
Let’s take a closer look at each file format for external drives for your Mac.
APFS (Apple File System)
APFS is the format introduced by Apple in early 2017 for iOS devices. APFS replaced the outdated macOS file system called HFS Plus. All new Macs are already bundled with APFS.
The main advantage of APFS is the fast speed of copying, pasting, and doing other operations on a disk. APFS also pays a lot of attention to technologies such as encryption, as well as improving work with metadata.
By default, APFS is optimized for solid-state drives (SSDs) and flash drives, however, it can also be used for traditional mechanical hard drives (HDDs). If you have an external SSD or a new USB stick and you definitely are not going to use them with Windows computers, you can choose this option.
Cons of APFS: As of now, APFS cannot be used to back up data using Time Machine.
Suitable: For macOS system drives, hybrid drives, SSDs, and flash drives that are only used on macOS.
Not Suitable: For disks used with older Macs or for Windows and Linux.
HFS Plus (Mac OS Extended)
HFS Plus (Hierarchical File System Plus) was used for Mac computers before APFS was introduced. If you bought a Mac before 2017 and haven’t updated it since then, it probably supports an HFS Plus drive. Mac OS Extended supports encryption and password protection.
Cons of HFS Plus: It is not supported on Windows computers until you install additional paid software like Paragon HFS Plus for Windows.
Suitable: For old Macs and old macOS systems (before 2017) or for mechanical hard drives and SSDs.
Not suitable: For Windows and Linux.
exFAT (Extended File Allocation Table)
The exFAT format is a file system that was created by Microsoft and supports both Windows and macOS operating systems. The exFAT offers similar compatibility as FAT32, however, it doesn’t have any of the annoying limitations that FAT32 has. For example, FAT32 supports files up to 4GB.
If you are definitely going to use an external drive or flash drive with both Windows and Mac computers, choose exFAT when formatting your drive. The exFAT format is an excellent “hybrid” for two computer worlds.
Suitable: For drives that are used on both Mac and Windows.
Not Suitable: For drives primarily used on Macs.
NTFS (Windows NT File System)
This is a Microsoft file system that allows you to read and write information in Windows. On macOS, you can only read NTFS-formatted disks. To be able to write on the NTFS external drive on your Mac, you will have to use additional paid software tools such as, for example, Paragon NTFS.
Thus, if you are not going to take any actions on your external drive connected to your Mac, or if you want to protect writing on it when giving the drive to anyone, you can choose NTFS when formatting your external drive.
Suitable: Reading and writing on Windows, only reading on macOS, and writing on macOS with additional software.
In summary: NTFS or exFAT?
Well, it seems that exFAT is the most optimal option for formatting a hard drive and fully using it with Windows and macOS. Unlike NTFS, you can not only read exFAT-formatted disks on Mac, but you can also get “write” access.
How to format an external drive (USB) for a Mac
The process of formatting a disk on the latest Mac OS versions is simple and intuitive. However, we will clarify a few moments to which you should pay attention. The provided steps are relevant for any Mac media. You can use them to format internal Mac drives, external HDD/SSD, or even a USB flash drive.
Steps for how to format an external drive on a Mac
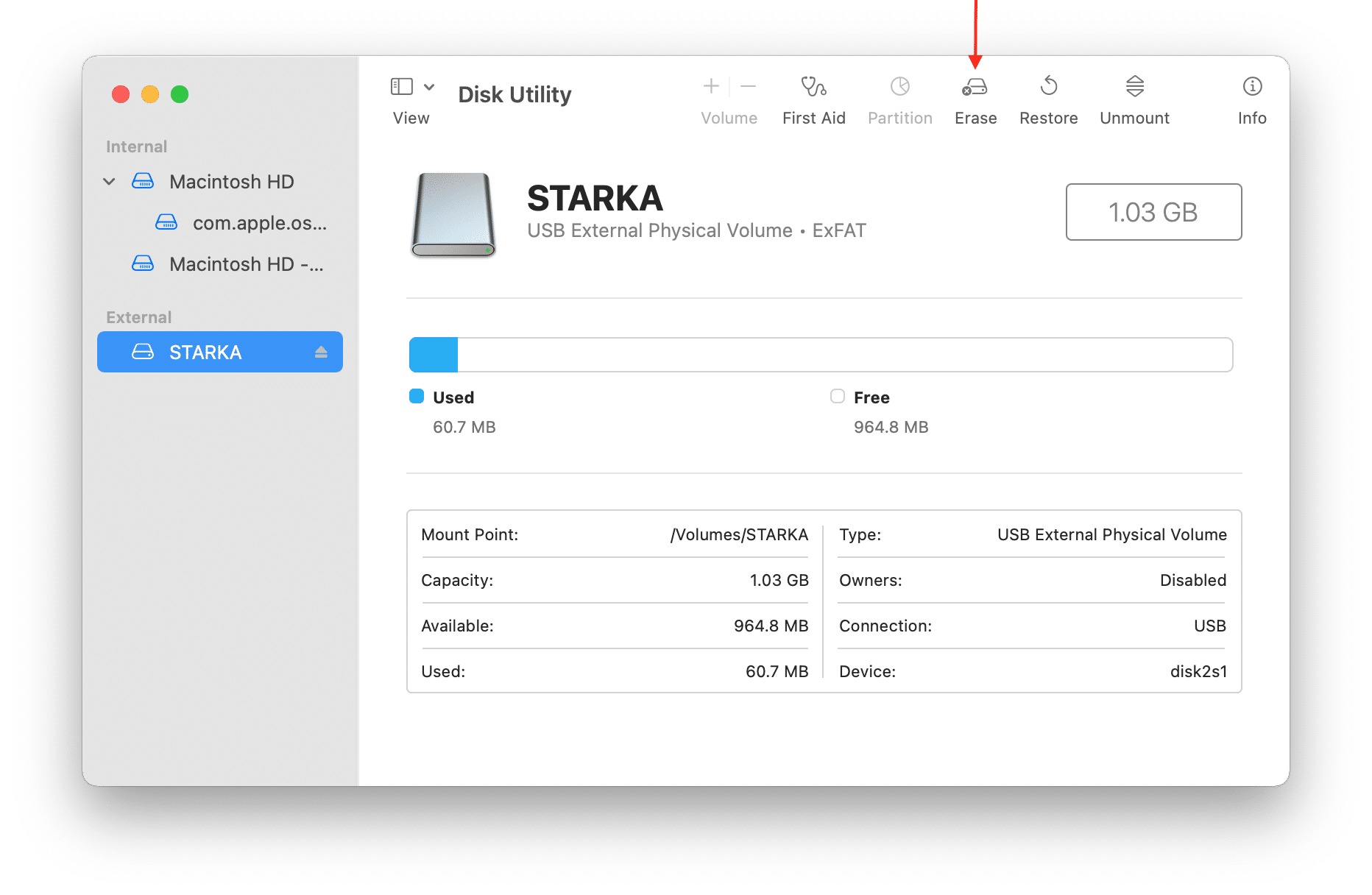
- Open the default Apple application called Disk Utility.
- Select your disk in the left sidebar.
- Click on Erase on the top.
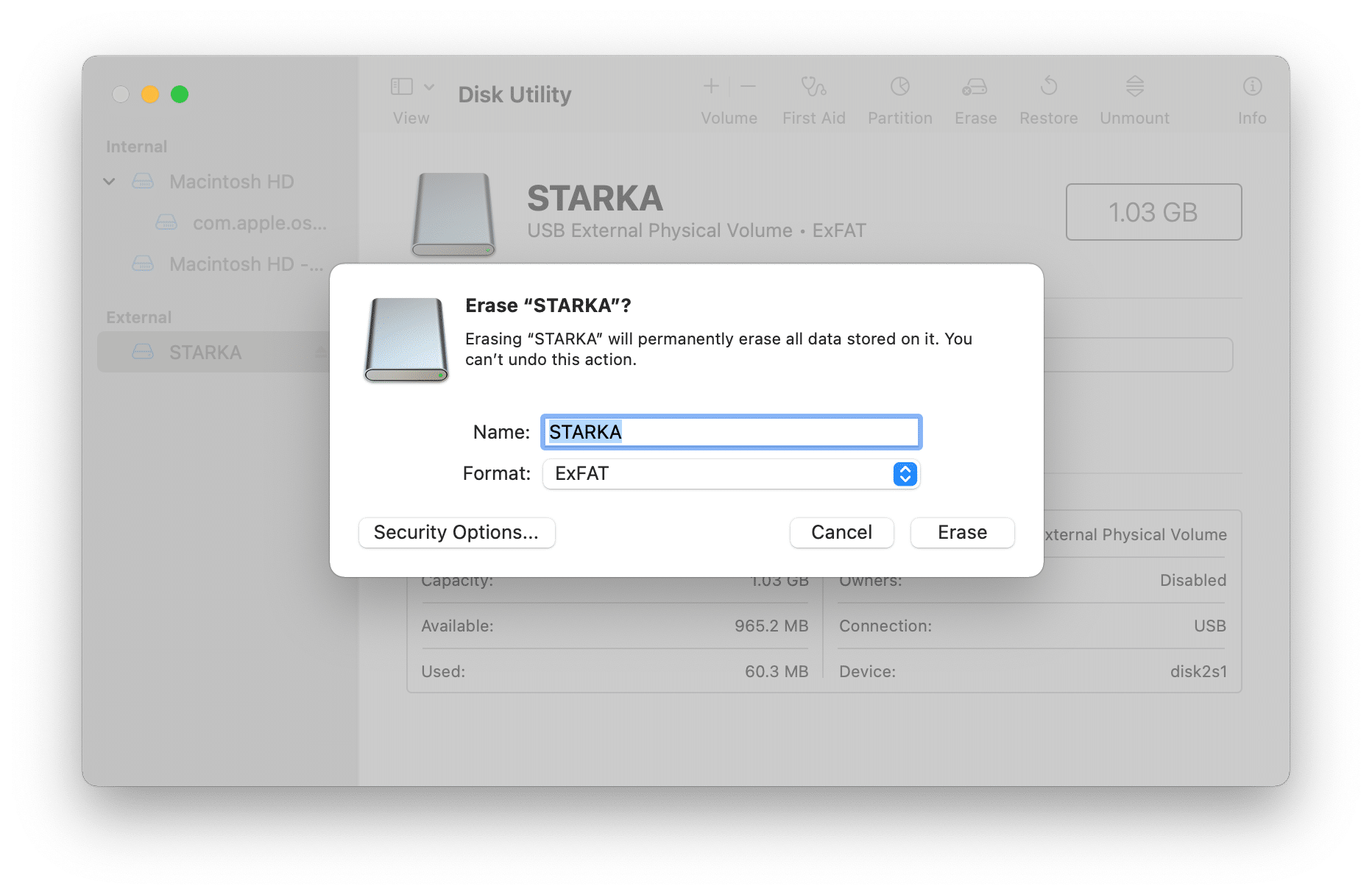
Important note: All your data on the external disk will be erased. If necessary, first copy your important data.
- In the window that appears, select the format and click Erase.
The formatting time depends on the volume of data being erased. Once it is finished, you should see the drive’s new file system type.
We want to remind you, that when you format your drive, all the data on it will be erased. You should back up your data before formatting the disk. If you haven’t made a backup, you can try using Mac data recovery software tools.
That’s all. We hope our guide helped you choose the best format for your external drive.