October 24, 2025
A chronological list of macOS versions in order
The Apple operation system (macOS) has a long history of innovation and evolution, dating back to its origins as Mac OS X in 2001. In this article, we will provide a chronological list of macOS versions in order and highlight some of their key features and changes.
macOS versions history
macOS is the operating system designed to run on Apple laptops and desktop computers. It was first launched in 2001 as Mac OS X, with the code name “Cheetah.” Apple has been naming its macOS updates after various locations in California, a trend that began with OS X Mavericks in 2013. The naming convention reflects Apple’s California heritage and is often inspired by the state’s natural landmarks or features.
Apple typically releases a major macOS update annually, usually during its Worldwide Developers Conference (WWDC) in June. During WWDC, Apple previews the upcoming macOS version, highlighting new features, improvements, and design changes. Following the announcement, developers gain access to beta versions to test and prepare their applications for the official release.
The yearly release cycle allows Apple to introduce new technologies and improvements regularly, keeping the operating system up-to-date with the latest advancements in hardware and software. It also helps ensure that users have access to the latest features and security updates.
A list of macOS versions
Here’s a brief overview of Mac updates in order and their corresponding release years up to macOS Sonoma:
- OS X 10 Kodiak (public beta 10.0) – released in 2000
- Mac OS X Cheetah (10.0) – released in 2001
- Mac OS X Puma (10.1) – released in 2001
- Mac OS X Jaguar (10.2) – released in 2002
- Mac OS X Panther (10.3) – released in 2003
- Mac OS X Tiger (10.4) – released in 2005
- Mac OS X Leopard (10.5) – released in 2007
- Mac OS X Snow Leopard (10.6) – released in 2009
- OS X Lion (10.7) – released in 2011
- OS X Mountain Lion (10.8) – released in 2012
- OS X Mavericks (10.9) – released in 2013
- OS X Yosemite (10.10) – released in 2014
- OS X El Capitan (10.11) – released in 2015
- macOS Sierra (10.12) – the first macOS version, dropped the “OS X” branding, released in 2016
- macOS High Sierra (10.13) – released in 2017
- macOS Mojave (10.14) – released in 2018
- macOS Catalina (10.15) – released in 2019
- macOS Big Sur (11.0) – significant update that marked the shift from version 10.x to 11.x, released in 2020
- macOS Monterey (12.0) – released in 2021
- macOS Ventura (13.0) – released in 2022
- macOS Sonoma (14.0) – released in 2023
- macOS Sequoia (15.0) – released in 2024
- macOS Tahoe (26.0) – released in 2025
Now let’s dive into short sum-ups of key improvements and innovations that Apple made along the way.
Mac OS X 10.0 Cheetah
The first public release of Mac OS X was a major milestone for Apple, as it marked the transition from the classic Mac OS to a new Unix-based platform. Mac OS X 10.0 Cheetah introduced the Aqua interface, which featured a water-themed design with translucent elements, drop shadows, and animations. Cheetah also brought some new applications, such as Mail, Address Book, TextEdit, and Sherlock.
Mac OS X 10.1 Puma
Mac OS X 10.1 Puma added support for DVD playback and burning, simplified Finder windows, enhanced printer and network support, and faster graphics and boot times. Puma also included some new applications, such as Image Capture and Internet Explorer for Mac.
Mac OS X 10.2 Jaguar
The third release of Mac OS X added more functionality and polish to the system, as well as some new technologies. Mac OS X 10.2 Jaguar introduced Quartz Extreme, which offloaded graphics rendering to the GPU for smoother performance. Jaguar also added support for MPEG-4 video in QuickTime, handwriting recognition with Inkwell, accessibility features with Universal Access, and a system-wide search tool called Finder Search.
Mac OS X 10.3 Panther
The fourth release introduced Exposé, which allowed users to quickly view and switch between all open windows and applications. Panther also added support for video conferencing in iChat AV, fast user switching, FileVault encryption, Safari web browser, Font Book, and Xcode development environment. Some of the new applications in Panther were Preview, iSync, iPhoto 2, iTunes 4, GarageBand, and iMovie 3.
Mac OS X 10.4 Tiger
It was one of the most successful and influential versions of the system, as it introduced many new features and technologies that are still used today, including Spotlight, which allowed users to search for files and information across the system and applications. Tiger also added support for Dashboard widgets, which provided quick access to various functions and information. Some of the new applications in Tiger were Automator, VoiceOver, Dictionary, Grapher, Front Row, Photo Booth, iPhoto 5, and iTunes 6.
Mac OS X 10.6 Snow Leopard
This release was focused on refining and optimizing the existing system rather than introducing major new features. Snow Leopard was designed to run faster and occupy less disk space, making it an ideal upgrade for older Macs. It also marked the transition to Intel-only architecture, dropping support for PowerPC-based Macs and included a 64-bit kernel, Safari 4, and native support for Microsoft Exchange.
OS X 10.7 Lion
Lion was a major release and, aimed to bring a more intuitive and iOS-inspired experience to the Mac. It introduced features like Launchpad for a gesture-based app launcher and Mission Control for unified window and application management. The Mac App Store made its debut, simplifying the process of discovering and installing applications. Lion emphasized full-screen apps and gestures, making navigation more intuitive.
OS X 10.8 Mountain Lion
This upgrade continued the trend of integrating iOS features into the Mac environment. It further emphasized iCloud integration, allowing seamless synchronization of documents and data across multiple Apple devices. Mountain Lion introduced the Notification Center for consolidated alerts and messages, as well as Gatekeeper for enhanced security through app certification. AirPlay Mirroring enabled wireless display sharing with an Apple TV, and Power Nap allowed Macs to update and perform tasks while in sleep mode. Messages replaced iChat for unified messaging, and Game Center brought gaming to the Mac platform.
OS X 10.9 Mavericks
The tenth major release focused on improving performance and energy efficiency, introducing features inspired by iOS. It introduced App Nap to conserve energy by prioritizing resources for active apps, and Compressed Memory for better utilization of system memory. Mavericks also marked the shift to naming the OS X versions after California locations. Finder Tabs streamlined file organization, and Tags enhanced content categorization. It added iBooks and Apple Maps for the first time on the Mac platform.
OS X 10.10 Yosemite
This version brought a significant visual overhaul to the Mac interface, aligning it more closely with the design language of iOS 7. Apple added more features to enhance collaboration between Macs and iOS devices. Handoff allowed seamless transfer of activities between devices, and iCloud Drive facilitated file sharing across platforms. Spotlight was improved, providing more intelligent and expansive search capabilities. Safari received a redesign.
macOS 10.11 El Capitan
It introduced Split View for enhanced multitasking, allowing users to work with two apps side by side in full screen. Mission Control received an upgrade, providing a more organized view of open apps and desktops. The system has a graphics technology to improve performance in graphic-intensive tasks. El Capitan also included enhancements to Safari, Mail, and Notes. System Integrity Protection (SIP) was introduced for added security by restricting root-level access to certain system files.
macOS 10.12 Sierra
Sierra continued the trend of integration between macOS and iOS devices. Siri made its debut on the Mac, bringing voice-activated assistance to the desktop. Universal Clipboard allowed seamless copying and pasting across Apple devices. Sierra also introduced the Apple File System (APFS) for improved file management and optimization. The system has got the Optimize storage management, as well as a desktop and Documents folder synchronization through iCloud.
macOS High Sierra (10.13)
High Sierra brought refining the macOS experience and improving system performance. The transition to the Apple File System (APFS) was completed, bringing advanced file management and encryption capabilities. In this macOS version, Safari received updates, including autoplay video blocking and Intelligent Tracking Prevention. Photos and Mail got improvements, and support for external graphics processors (eGPUs) was introduced.
macOS Mojave (10.14)
The fifteenth release, Mojave, brought a dark mode to the macOS interface for the first time, providing users with a visually striking alternative. Dynamic Desktop allowed wallpapers to change based on the time of day. Desktop Stacks streamlined cluttered desktops by organizing files automatically. The Mac App Store underwent a redesign for improved discoverability, and new apps such as News, Stocks, Voice Memos, and Home made their debut on the Mac.
macOS Catalina (10.15)
This release brought several significant changes to macOS. The iTunes app was replaced by three separate apps – Apple Music, Apple TV, and Apple Podcasts. Apple introduced a Sidecar that allowed users to use an iPad as a secondary display or drawing tablet. Catalina also marked the end of support for 32-bit apps, emphasizing the shift to 64-bit architecture. The Find My app was combined with Find My iPhone and Find My Friends for a better location-tracking experience.
macOS Big Sur (11.0)
With Big Sur, the system brought a significant visual overhaul, featuring a refined interface with rounded corners, new icons, and vibrant color schemes. It introduces the Control Center, providing quick access to system controls. Safari underwent a major redesign for improved speed and efficiency. Messages gained new features, including inline replies and pinned conversations.
macOS Monterey (12.0)
Monterey continued the trend of integrating macOS with other Apple devices. Universal Control allowed seamless control of multiple Apple devices with a single mouse and keyboard. Shortcuts, a popular iOS feature, made its debut on the Mac for the automation of tasks. AirPlay to Mac enabled users to share content from iPhone or iPad directly to the Mac. Safari received updates, including a new tab bar and grouped tabs. Live Text allowed users to interact with text in images and photos. A new feature was the Focus which was designed to help users manage notifications based on their activities.
macOS Ventura (13.0)
Ventura introduced a redesigned Control Center with more customization options and quick access to key features. The system sounds were redesigned and the Privacy features received additional attention, with more detailed tracking reports and improved app permissions. Ventura continued the integration of iOS-inspired design elements, providing a cohesive user experience across Apple devices.
macOS Sonoma (14.0)
Sonoma introduced innovations in augmented reality (AR) applications, leveraging Apple’s ARKit. The Siri voice assistant received enhanced natural language processing capabilities. System-wide gestures and navigation were refined for a more intuitive user experience. Sonoma also emphasized sustainability, introducing features to monitor and reduce the environmental impact of device usage.
macOS Sequoia (15.0)
macOS Sequoia, released in 2024, has a fresh look with small design changes, better battery life, and more support for gaming and high-performance apps. New features include better multitasking, a more powerful Spotlight search with AI, and improved continuity to make switching between Apple devices easier.
macOS Tahoe (26.0)
macOS Tahoe, released in September 2025, marks a significant step forward in personalization, productivity, and intelligent features for Apple’s desktop platform. The design overhaul centers on Liquid Glass aesthetics, making the entire interface more translucent and visually immersive.
Control Center bacame fully customizable, allowing easy arrangement of shortcuts from both Mac and iPhone apps, including third-party tools, and even multiple control pages for streamlined workflows.
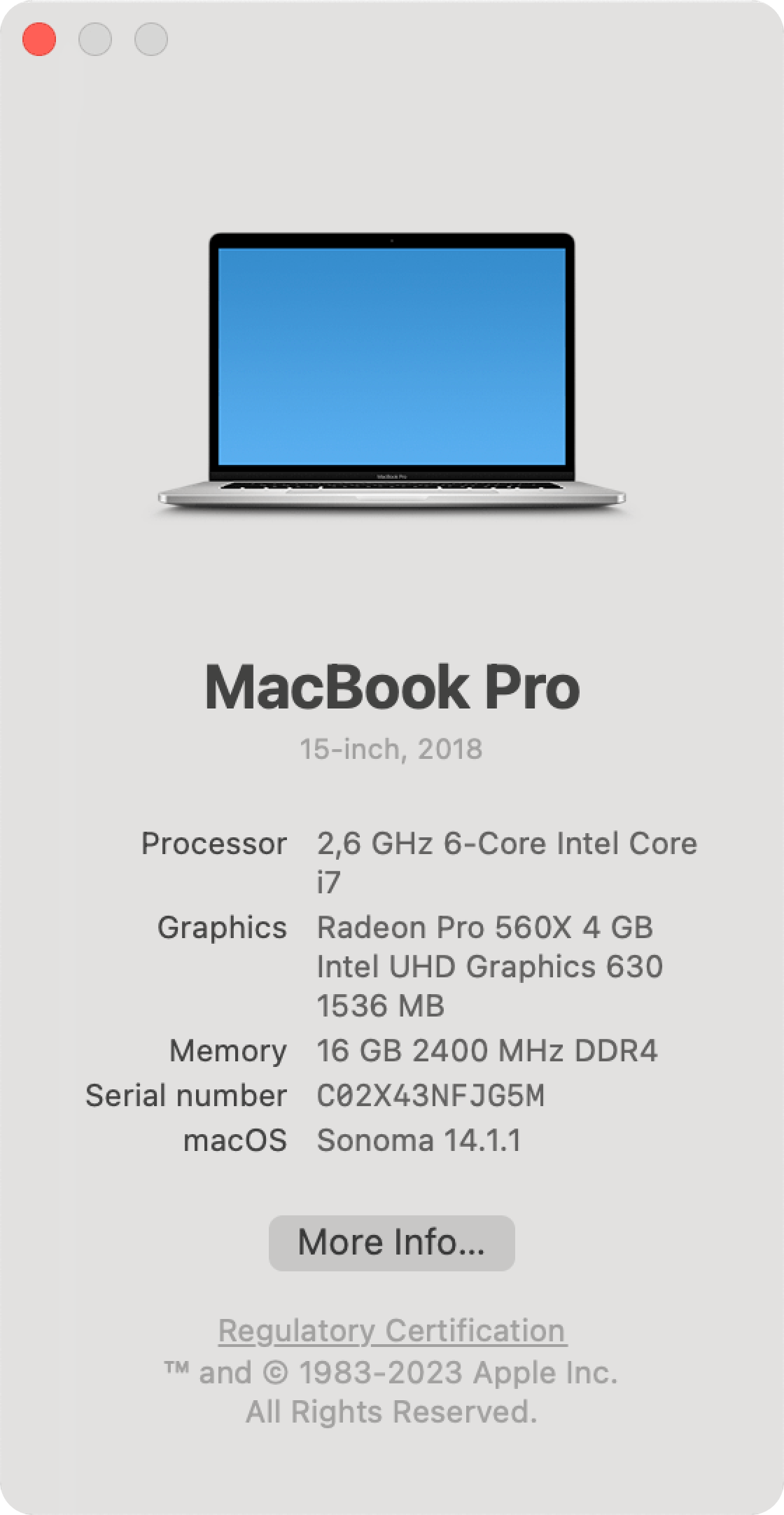
How to check the latest macOS on your computer
To check what the latest macOS version is installed on your computer, you can follow these steps:
- Click on the Apple logo in the menu bar.
- Select About this Mac from the drop-down list.
- On the window that appears, you can see the information about your Mac, including the model, processor, memory, and the macOS version.
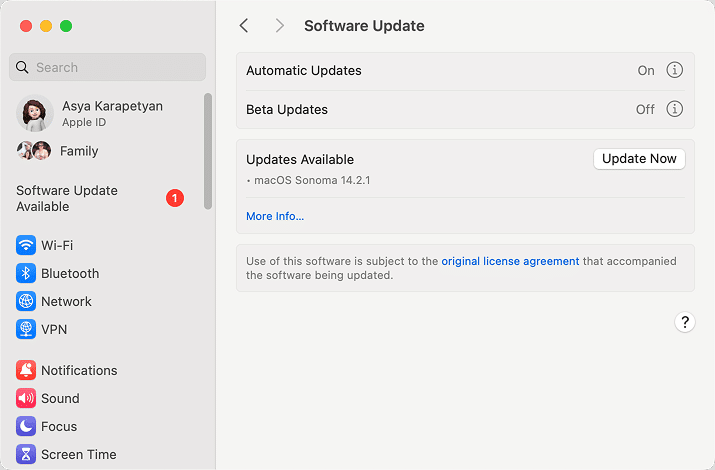
How to update your Mac
To check your macOS for updates and install the latest version, follow these steps:
- Open System Settings on your Mac.
- Click General in the left panel.
- Click Software Update in the right panel.
- If there are updates available, you will see the option to “Upgrade Now” or “Update” depending on your macOS version. Follow the on-screen instructions to install the updates.
Note:
If your Mac is running an older macOS version and is not compatible with the latest release, you won’t see the update option for the newest macOS version. In that case, you may need to check the system requirements for the latest macOS and consider upgrading your hardware if necessary.
Conclusion
We have reviewed the history of Mac operating systems and also highlighted some of the main features and improvements that each version introduced, such as the Aqua interface, the Finder search, the Universal Access, and the iCloud integration. We hope this article has been informative and useful for anyone interested in learning more about the macOS timeline.